Types of Nursing Specialties
Types of Nursing Specialties
The nursing field is diverse and dynamic, encompassing a wide array of specialized roles and responsibilities. These nursing specialties have evolved in response to the ever-changing healthcare landscape and the need for highly skilled nursing professionals to cater to specific patient populations and healthcare challenges. While the image of a nurse in a white uniform attending to patients in a hospital remains iconic, the reality is that nursing encompasses a vast range of roles that extend beyond traditional bedside care.
In this article, we will delve into the world of nursing specialties, exploring how nurses have developed their expertise to provide specialized care, support, and knowledge. Each nursing specialty addresses unique patient needs, ranging from infants to the elderly and from mental health to critical care. These specialized nurses play an essential role in the healthcare system, contributing to better patient outcomes, improved healthcare quality, and enhanced patient experiences.
As we explore the types of nurses’ specialties, we will highlight the core responsibilities and challenges nurses face in each field. From the fast-paced intensity of critical care units to the compassionate support provided in palliative care settings, we will examine the key attributes required to excel in each specialized role.
Overview of Nursing Specialties
Nursing specialties refer to specialized areas within the nursing profession where nurses focus on specific patient populations, medical conditions, or healthcare settings. These specialties are born out of the need to provide expert care tailored to the unique needs of patients in various healthcare scenarios. While general nursing practice equips nurses with fundamental knowledge and skills to care for a diverse range of patients, nursing specialties take that expertise to a higher level by honing in on particular areas of healthcare.
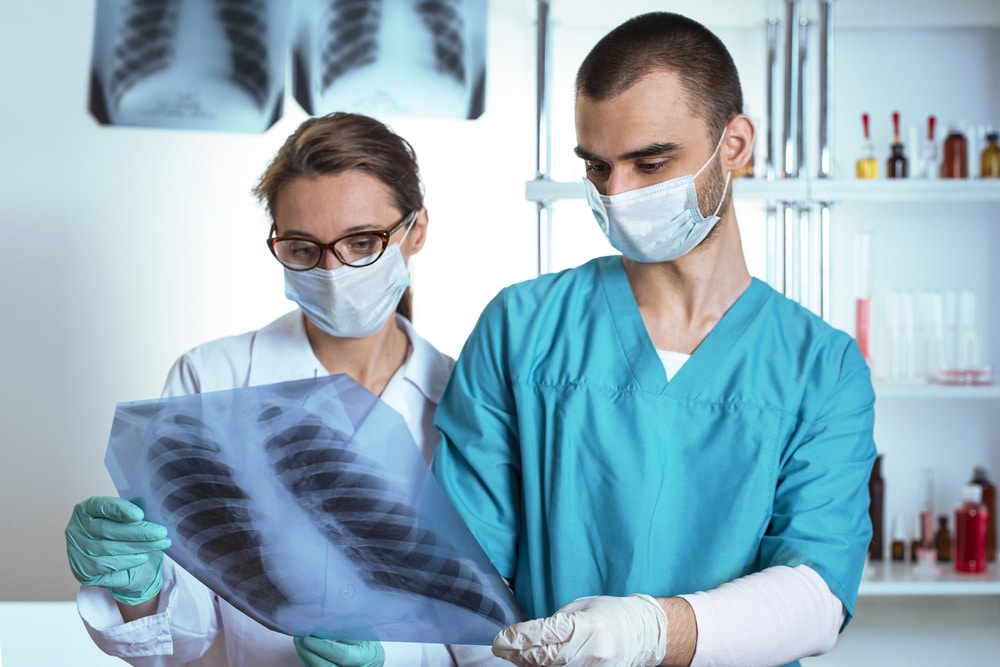

Nurses specializing in a particular field undergo additional education, training, and certification to build proficiency. Specialization allows nurses to become subject matter experts, developing a deeper understanding of the intricacies and challenges specific to their chosen specialty. This expertise positions them to deliver more precise and comprehensive care, contributing to better patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare services.
Historical Development of Nurse Specialties
The concept of nursing specialties has evolved in response to the changing demands of healthcare and the recognition of the diverse needs of patients. Historically, nursing was viewed as predominantly female, and nurses were often associated with providing care at the bedside in hospitals. As medical knowledge expanded and healthcare systems became more complex, the need for specialized nursing roles emerged.
In the mid-19th century, Florence Nightingale, often considered the founder of modern nursing, revolutionized the nursing profession during the Crimean War. Her emphasis on sanitation, hygiene, and systematic nursing practices set the stage for the professionalization of nursing. While Nightingale’s contributions significantly shaped general nursing practice, the idea of nursing specialties was fully realized in the 20th century.
The advent of advanced medical technologies and treatments in the 20th century necessitated specialized nursing roles. Critical care units were established to cater to acutely ill patients, developing critical care nursing as a distinct specialty. The increase in births and advancements in obstetric care brought about the specialization of obstetric and gynecological nursing. Likewise, recognizing mental health as a crucial component of overall well-being resulted in the growth of psychiatric-mental health nursing.
Advantages and Benefits of Nursing Specialization
The specialization of nursing offers numerous advantages and benefits to both nurses and patients:
Expertise
Specialized nurses possess in-depth knowledge and skills in their chosen field, allowing them to provide targeted and high-quality care to patients.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Specialized care leads to better patient outcomes, as nurses can focus on evidence-based practices and interventions specific to their specialty.
Career Advancement
Nursing specialties provide opportunities for career advancement, leadership roles, and increased earning potential.
Job Satisfaction
Nurses who work in their preferred specialties often report higher job satisfaction due to their passion for the specific area of healthcare.
Addressing Specific Needs
Nursing specialties address the unique needs of diverse patient populations, including children, elderly individuals, and those with specific medical conditions.
Advancement of Healthcare
Specialized nurses contribute to advancements in healthcare by participating in research, innovation, and the development of best practices within their specialties.
Diversity in Nursing
Specialties add diversity to nursing, attracting individuals with various interests and backgrounds and enriching the healthcare landscape.
Nurse specialties play a vital role in meeting patients’ and communities’ complex and diverse healthcare needs. These specialized roles have developed over time in response to the evolution of healthcare, advancing medical technologies, and the recognition of unique patient requirements.
Popular Nursing Specialties
Nursing is a dynamic and diverse profession, offering numerous specialized areas of practice to meet the specific healthcare needs of patients. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, certain nursing specialties have become particularly popular due to their importance and relevance in addressing critical healthcare challenges. Below are some of the most popular nursing specialties:
1. Medical-Surgical Nursing
Medical-surgical nurses are among the most common and versatile specialty nurses. They care for adult patients with various medical conditions, post-surgery, or those in need of acute care. Medical-surgical nurses work in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings, providing comprehensive and holistic care to patients.
2. Pediatric Nursing
Pediatric nurses specialize in caring for infants, children, and adolescents. They have expertise in assessing the unique needs of young patients, providing age-appropriate care, and offering support to their families. Pediatric nurses work in pediatric hospitals, pediatric wards, and other healthcare facilities catering to children.
4. Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing
Obstetric and gynecological nurses focus on women’s health throughout their reproductive years. They provide care during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, as well as address gynecological conditions and family planning. These nurses work in labor and delivery units, maternal-fetal medicine clinics, and women’s health centers.
5. Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing
Psychiatric nurses specialize in caring for individuals with mental health disorders. They provide support, counseling, and medication management to patients with conditions like depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and addiction. Psychiatric nurses work in psychiatric hospitals, community mental health centers, and addiction treatment facilities.
6. Critical Care Nursing
Critical care nurses work in intensive care units (ICUs) and provide specialized care to critically ill or unstable patients. They are trained to handle complex medical conditions, utilize advanced life support technologies, and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations.
7. Nurse Anesthetists
Nurse anesthetists are advanced practice nurses specializing in anesthesia administration. They work closely with anesthesia teams to administer anesthesia during surgeries and medical procedures, ensuring patients’ safety and comfort during the perioperative period.
8. Nurse Practitioners
Nurse practitioners (NPs) are advanced practice registered nurses who have completed additional education and training. They have the authority to diagnose and treat medical conditions, prescribe medications, and provide primary and specialized care. Nurse practitioners work in various settings, including primary care clinics, specialty clinics, and hospitals.
9. Informatics Nursing
Informatics nurses bridge the gap between healthcare and technology. They manage and utilize healthcare data and information systems to improve patient care, enhance efficiency, and ensure the security and privacy of sensitive medical information.
8. Geriatric Nursing
Geriatric nurses specialize in caring for elderly patients, addressing age-related health issues, and promoting healthy aging. They work in geriatric care facilities, assisted living centers, and long-term care settings.
9. Palliative Care Nursing
Palliative care nurses focus on providing comfort and support to patients with serious illnesses, focusing on symptom management, pain relief, and improving the quality of life for patients and their families.
These popular nursing specialties represent just a selection of diverse and rewarding career paths. Each specialty requires unique skills, knowledge, and a passion for delivering specialized care, contributing to better patient outcomes and improved healthcare services. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, these specialties will remain in high demand, attracting dedicated and compassionate nurses seeking to make a significant difference in the lives of their patients.
Pediatric Nursing
Pediatric nursing is a specialized branch of nursing degree that focuses on providing comprehensive care to infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatric nurses play a crucial role in promoting the health and well-being of young patients, ranging from newborns to teenagers, by addressing their physical, emotional, and developmental needs. These nurses work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, pediatrician offices, schools, and other healthcare facilities catering to children.

Roles and Responsibilities of Pediatric Nurses:
- Health Assessment: Pediatric nurses conduct thorough health assessments to monitor children’s growth and development, identify potential health issues, and initiate early interventions.
- Vaccination and Immunization: Following national immunization schedules, pediatric nurses administer vaccinations and immunizations to protect children from preventable diseases.
- Medication Management: They administer medications and educate parents and caregivers about proper dosages, side effects, and precautions.
- Pain Management: Pediatric nurses use age-appropriate pain management techniques and emotionally support children during painful procedures or illnesses.
- Family Education: They educate parents and caregivers about child health, growth milestones, nutrition, and disease prevention, empowering them to care for their children effectively.
- Child Advocacy: Pediatric nurses act as advocates for their young patients, ensuring their rights, safety, and best interests are protected throughout their healthcare journey.
- Pediatric Emergency Care: They are trained to respond quickly and efficiently to children’s medical emergencies, providing life-saving interventions and stabilizing patients.
- Pediatric Specialties: Some pediatric nurses specialize in areas such as pediatric oncology, pediatric cardiology, pediatric intensive care, or neonatal nursing, providing specialized care to children with specific medical conditions.
Unique Challenges in Pediatric Nursing:
Pediatric nursing comes with its own set of challenges due to the nature of caring for young patients:
- Communication: Pediatric nurses must be skilled in communicating effectively with children of different ages, as well as their parents or guardians, to establish trust and rapport.
- Emotional Resilience: Caring for sick or injured children can be emotionally challenging, requiring nurses to cope with stress and provide support to families facing difficult situations.
- Pain Management: Managing pain in children can be complex, as their ability to express discomfort may vary with age and development.
- Family Involvement: Pediatric nurses must involve and collaborate with families in the child’s care plan, respecting their preferences and cultural beliefs.
Rewards and Fulfillment:
Pediatric nursing can be immensely rewarding, offering the opportunity to impact children’s lives and their families positively. The joy of seeing children recover and thrive under their care gives pediatric nurses a sense of fulfillment. Building strong bonds with young patients and their families and witnessing the resilience of children in the face of adversity are deeply gratifying aspects of this specialty.
Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing
Obstetric and gynecological nursing, often abbreviated as OB/GYN nursing or perinatal nursing, is a specialized branch of nursing that focuses on providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Obstetric and gynecological nurses play a vital role in supporting women’s health and ensuring safe and positive pregnancy experiences.
Roles and Responsibilities of Obstetric and Gynecological Nurses:
- Prenatal Care: Obstetric nurses provide prenatal care to pregnant women, conducting regular check-ups, monitoring fetal development, and educating mothers about healthy pregnancy practices.
- Labor and Delivery Assistance: During childbirth, these nurses assist obstetricians and midwives, providing comfort measures, monitoring fetal and maternal well-being, and advocating for the patient’s birth plan.
- Postpartum Care: Obstetric nurses continue to care for women after childbirth, providing postpartum assessments, supporting breastfeeding, and offering guidance on newborn care and parenting.
- Neonatal Care: In some cases, obstetric nurses may provide care to premature or critically ill newborns in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) or special care nurseries.
- Gynecological Examinations: Obstetric and gynecological nurses perform gynecological examinations, including Pap smears, breast exams, and assessments for reproductive health issues.
- Women’s Health Education: They educate women about family planning, contraception, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and other aspects of reproductive health.
- Support during Gynecological Procedures: These nurses assist healthcare providers during gynecological procedures, such as colposcopies or biopsies.
- Fertility and Infertility Care: Obstetric and gynecological nurses may be involved in fertility clinics, providing care to women seeking reproductive assistance, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Challenges and Rewards in Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing:
Obstetric and gynecological nursing can present unique challenges due to the emotionally charged nature of pregnancy, childbirth, and gynecological care. Nurses may encounter high-stress situations, complications during labor, and the potential for perinatal loss. Providing support and empathy to women and their families during difficult times is essential to this nursing specialty.
However, the rewards of obstetric and gynecological nursing are equally significant. Being part of the miracle of birth and helping women navigate the journey of motherhood brings immense satisfaction. Obstetric and gynecological nurses are vital in promoting positive birth experiences, healthy pregnancies, and improved maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Importance of Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing:
Obstetric and gynecological nursing is essential in ensuring the well-being of women during critical stages of their lives. It is key in promoting maternal and child health, reducing maternal and infant mortality, and empowering women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health. The expertise of obstetric and gynecological nurses is instrumental in the early detection and management of pregnancy-related complications, thereby improving overall pregnancy outcomes.
Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing
Psychiatric-mental health nursing is a specialized branch that focuses on providing care and support to individuals with mental health disorders. These nurses are vital in promoting mental wellness, assessing patients’ emotional needs, and assisting with treatment plans.
Through therapeutic communication and compassionate care, psychiatric-mental health nurses help patients cope with their conditions, manage symptoms, and work toward recovery. Their expertise in addressing mental health stigma and providing holistic care contributes to the overall well-being of individuals and their families.
Critical Care Nursing
Critical care nursing is a specialized area that involves providing intensive and specialized care to patients with life-threatening conditions or complex medical needs. Critical care nurses work in critical care units (CCUs) or intensive care units (ICUs) in hospitals, where they closely monitor patients, administer critical medications, and utilize advanced medical technology to stabilize and support patients’ vital functions.
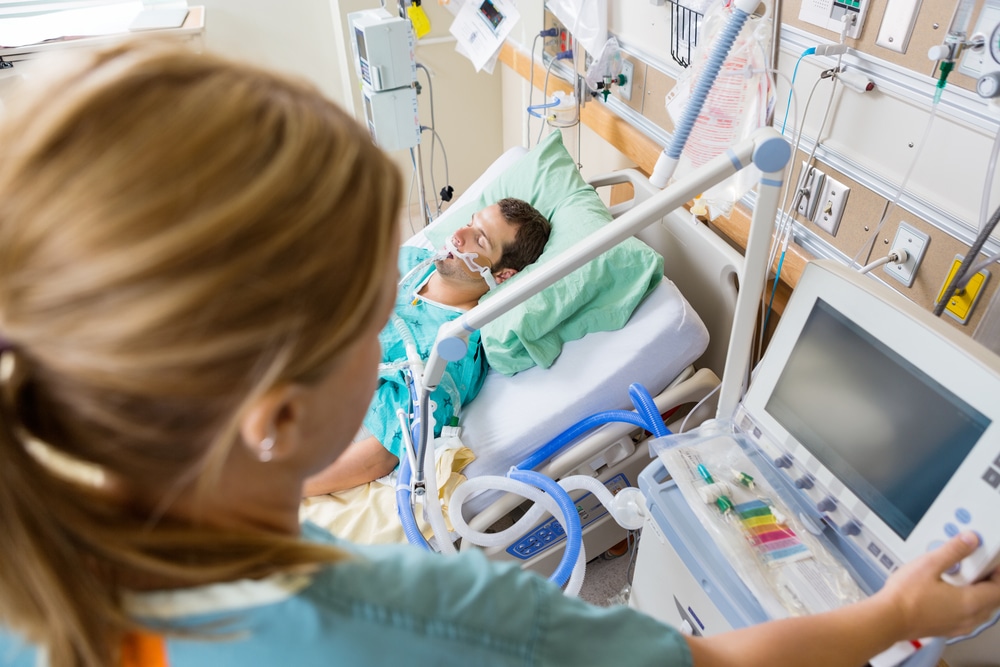

These highly skilled nurses are trained to respond swiftly to emergencies, make quick decisions, and collaborate with healthcare teams to ensure the best possible outcomes for critically ill patients. Their dedication, expertise, and compassion play a crucial role in saving lives and providing critical support during some of the most challenging moments in healthcare.
Nurse Midwives
Nurse midwives are advanced practice nurses who specialize in providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. They play a crucial role in supporting and empowering women throughout the birthing process, offering personalized care and guidance to ensure healthy pregnancies and positive birth experiences.
Nurse midwives perform deliveries, provide prenatal and postnatal care, and address women’s gynecological needs. With their expertise in natural childbirth and a focus on holistic care, nurse midwives contribute significantly to women’s reproductive health and maternal well-being.
Emerging Specialties in Nursing
Emerging specialties in nursing represent exciting and evolving areas of practice that are gaining prominence in response to changing healthcare needs. These emerging fields often involve the integration of cutting-edge technology and innovative approaches to patient care.
Examples of emerging nursing specialties include informatics nursing, where nurses manage healthcare data and information systems to improve patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency, as well as genomics nursing, which focuses on applying genetic and genomic information to individualize patient care. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, these emerging specialties play a crucial role in advancing nursing practice and enhancing patient care outcomes.
Specialized Nursing Roles
Specialized nursing roles encompass advanced positions within the nursing profession, requiring additional education and training. Examples include:
- Certified registered nurse anesthetist.
- Certified nurse midwife.
- Family nurse practitioner.
- Clinical nurse specialist.
- Nurse educator.
- Psychiatric-mental health nurses.
- Geriatric nurses.
- Informatics nurses.
- ER, nurses.
- Critical care nurses.
These specialized nurses play critical roles in various healthcare settings, addressing specific patient needs and improving outcomes.
Specialized nursing roles come with unique challenges and rewards, making them both demanding and fulfilling nursing career paths.
Challenges
- Complexity of Care: Specialized nurses often deal with complex and challenging medical conditions, requiring advanced knowledge and critical thinking to manage patients’ health effectively.
- Emotional Stress: Working in specialized fields like critical care, psychiatric, or palliative care can expose nurses to emotionally challenging situations, such as dealing with life-threatening emergencies or end-of-life care.
- Continuous Learning: Specialized nurses must stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in their fields, necessitating ongoing education and professional development.
- High Responsibility: With specialized knowledge comes increased responsibility, as these nurses are accountable for making crucial decisions that can directly impact patients’ lives.
- Burnout Risk: The demanding nature of specialized nursing roles, coupled with the emotional toll, can increase the risk of burnout among these registered nurses.
Rewards
- Making a Difference: Specialized nurses have the opportunity to make a significant difference in the lives of their patients, often helping them through challenging times and facilitating their recovery.
- Expertise Recognition: Becoming an expert in a particular nursing specialty brings recognition and respect from colleagues, patients, and the healthcare community.
- Personal Fulfillment: The ability to provide specialized care and see positive outcomes can be deeply fulfilling for specialized nurses, contributing to job satisfaction.
- Career Advancement: Specialized nursing roles offer pathways for career advancement, including opportunities for leadership positions, research, and teaching.
- Meaningful Connections: Building strong bonds with patients and their families can create a profound sense of connection and purpose in specialized nursing.
- Positive Outcomes: Specialized nurses often witness the positive impact of their interventions, leading to improved patient outcomes and higher success rates.
Specialized nursing roles present their own set of challenges and rewards. While they demand dedication, continuous learning, and emotional resilience, the fulfillment of making a tangible difference in patients’ lives and recognizing expertise gratify these roles for passionate and dedicated nurses.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, nursing specialties encompass a wide range of expert care, catering to the unique needs of patients across diverse medical disciplines. From critical care and pediatrics to mental health and geriatrics, each specialty plays a vital role in ensuring the well-being of individuals at different stages of life and health conditions. Nurses’ unwavering dedication, compassion, and expertise profoundly impact healthcare outcomes, touching countless lives and fostering a healthier world.
These remarkable professionals form the backbone of the healthcare system, tirelessly working to provide the highest standard of care and support to patients and their families. Their commitment to lifelong learning, evidence-based practices, and patient advocacy propels the nursing profession forward, continually adapting to new challenges and advancements in medical knowledge and technology. Nurses, in all their diverse specialties, are the heart and soul of healthcare, and we owe them our deepest gratitude for their invaluable contributions.
Nursing Articles
- ¿Cómo obtengo un título de fisioterapia en los EE. UU.?
- 10 Best Nursing Schools in Phoenix in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- 5 Reasons Why You Should Become a CNA
- 6 Nursing Scholarships For All Students
- About Us
- Accelerated Nursing Programs In Utah: Everything You Need To Know
- ADN vs BSN – What You Need to Know
- Advance Your Nursing Career Today!
- Amazing Texas College Responses to COVID-19
- APRN Salary Trends: What To Expect In The Coming Years
- Are You Ready to Make a Difference in People’s Lives—Without Waiting Years to Get Started?
- Average Nurse Salary
- Becoming An HIV & AIDS Nurse
- Best 16 accelerated nursing programs in ny in 2024
- Best 22 LPN Programs in MA in 2024
- Best Accelerated BSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in 2024: Explore Options Today
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in Massachusetts in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best ADN to MSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Associate of Science in Nursing Degrees in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Degree Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Nursing Programs in Chicago in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Nursing Programs in Georgia in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Arizona in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in California in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Colorado in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Connecticut in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in GA in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Houston, Texas in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Illinois in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Los Angeles in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Maryland in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Massachusetts in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN programs in Michigan in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in MN in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in New Jersey (NJ) in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in New York in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in North Carolina in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Oklahoma in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Oregon in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in PA in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in San Antonio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in San Diego in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Texas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Utah in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Virginia in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Washington in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN to DNP Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CNA Classes
- Best CNA Programs in the U.S. in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Community College Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CRNA Schools in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CRNA Schools in Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Direct Entry MSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best DNP Degree Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best DNP Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best FNP Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Forensic Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Gifts for Nurses
- Best Healthcare Administration Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN Programs in Connecticut in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN to BSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN to RN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN/LVN to BSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LVN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Masters Degree in Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Medical Assistant Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Medical Billing Schools
- Best MSN Degree Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best MSN Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2024: Explore Options Today
- Best Nursing Careers: 50 Different Types of Nurses
- Best Nursing Degree Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Informatics Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in Athens, Georgia in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in Indianapolis in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing School in Broward in 2024
- Best Nursing School in Fort Lauderdale in 2024 (On-Campus or Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in 2024: Explore Your Options Today
- Best Nursing Schools in Alabama in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Alaska in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Albany, NY in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Albuquerque, NM in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arizona in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arkansas in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arlington Texas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Atlanta in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Augusta, GA in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Austin, Texas in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Baltimore in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Baton Rouge in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Birmingham AL in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Boca Raton in 2024
- Best Nursing Schools in Boston in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Brooklyn, NY in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in California in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Central Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Charlotte, NC in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Chicago in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Cincinnati, OH in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Cleveland, Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Colorado in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Colorado Springs in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Columbia, SC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Columbus Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Connecticut in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in D.C. in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Dallas in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Dayton, Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Delaware in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Denver Colorado in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Des Moines in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in El Paso, TX in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fayetteville, NC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fort Myers in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fort Worth, Texas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Georgia in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Greenville SC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Greenville, SC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Hawaii in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Houston in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Idaho in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Illinois in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Indiana in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Iowa in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Jacksonville FL in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kansas City in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kansas in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kentucky in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Lancaster, PA in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Las Vegas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Long Island, NY in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Los Angeles in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Louisiana in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Louisville, KY in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Maine in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Manhattan in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Maryland in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Massachusetts in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Memphis TN in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Miami in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Michigan in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Milwaukee in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Minneapolis in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Minnesota in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Mississippi in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Missouri in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Montana in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Montgomery, Alabama in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nashville TN in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nebraska in 2024 (On-Campus and Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nevada in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New England in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Hampshire in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Jersey in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Mexico in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Orleans in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New York in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools In North Carolina in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in North Dakota in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Northern California in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in NYC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oahu in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oklahoma City in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oklahoma in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Orange County in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools In Oregon in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Orlando Florida in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Pennsylvania in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Philadelphia in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Pittsburgh in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Portland, Oregon in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Queens in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Raleigh, NC in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Rhode Island in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Richmond VA in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Sacramento, CA in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Salt Lake City in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in San Antonio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in San Diego in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Savannah, GA in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Seattle WA in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Carolina in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Dakota in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Southern California in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Springfield, MO in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in St Louis, MO in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Tampa, Florida in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Tennessee in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Texas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the Bronx in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the Midwest in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the South in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Toledo, Ohio in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Utah in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Vermont in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Virginia Beach in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Virginia in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Washington in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in West Palm Beach FL in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in West Virginia in 2024 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Wisconsin in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Wyoming in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Online Nursing Programs in 2024: Explore Your Options Today
- Best Online RN to BSN Programs in 2024
- Best Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Phlebotomy Certification Programs in the U.S. in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Physician Assistant Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in 2024: The Complete List (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in California in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Florida in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Nebraska (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in North Carolina in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in NY in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Texas in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to MSN Online Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Second Degree Nursing Programs in 2024 (Online & On-Campus)
- BSN vs. MSN Guide: Which One is Better for You?
- Building a Bright Future: Exploring the Best Nursing Schools in Texas
- Cardiac Nurse Salary in 2024
- Charge Nurse vs. Nurse Manager: What’s the Difference?
- CNA Meaning – How To Become A Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA)?
- CNA Requirements and Career Outlook
- CNA Salary in 2024
- College Planning for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students
- College Resources for Students With Disabilities
- College Responses to COVID 19 in Kentucky
- College Responses to COVID 19 in South Dakota
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Iowa
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Maine
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Minnesota
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Rhode Island
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Vermont
- Colleges Responses to COVID-19 in Wisconsin
- Colleges’ Responses to COVID 19 in Nebraska
- Colleges’ Responses to COVID 19 in New Mexico
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Alabama
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Connecticut
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Hawaii
- Cómo convertirse en fisioterapeuta [Guía definitiva]
- Compact Nursing States List
- Critical Care Nursing Salary
- Dialysis Nurse Salary in 2024
- DNP Salary in 2024
- DNP vs. NP: What’s the Difference?
- Elevate Your Medical Career: Ultrasound Tech Program Near Me
- Emergency Room Nurse Salary in 2024
- Empower Your Career: Discover The Best Nurse Practitioner Programs
- Exploring the Aesthetic Nurse Salary: How Much Do Aesthetic Nurses Earn
- Exploring the Earnings: Associate Degree in Nursing Salary Insights
- Exploring The Forensic Nurse Salary: How Much Do Forensic Nurses Earn
- Find a Healthcare Program
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes Here
- Find CNA Classes Near You
- Find CNA Classes Near You
- Find CNA Programs Near You
- Find Direct Entry MSN Programs
- Find Home Health Aide Classes
- Find LPN Classes
- Find LPN Classes
- Find LVN/LPN Classes
- Find Medical Assistant Classes
- Find Medical Assistant Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes Near You
- Find Pharmacy Technician Classes Now
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find the Best CNA Classes
- Find the Best CNA Classes
- Find the Best Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find the Best Medical Billing And Coding Classes
- Find the Best Medical Billing Classes
- Find the Best Nursing Programs
- Find the Best Phlebotomy Classes
- Find the Best Phlebotomy Classes
- Find the Best Phlebotomy Classes
- Flight Nurse Salary in 2024
- FNP Salary Revealed: Your Path To Lucrative Earnings
- FNP vs. ACNP in 2024
- FNP-BC vs. FNP-C: Learn the Difference Between These Nurse Practitioner Certifications
- Guide to Financial Aid
- Guiding The Heart: Ethical Principles In Nursing Practice
- Healthcare Champions In The Classroom: Exploring School Nurses Salary Trends
- Highest Paying Nursing Careers in 2024
- Highest Paying Telehealth Nursing Jobs
- Home health care Nurse in 2024
- Hospice Nurse Salary Trends And Outlook: What To Expect
- How Long Is Nursing School?
- How Much Do Nurses Make?
- How Much Do Travel Nurses Make?
- How Much Does A Nurse Practitioner Make?
- How Much Does A Travel Nurse Make
- How Much Does Nursing School Cost
- How to Become a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- How to Become a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- How to Become a CNA
- How to Become a CRNA in 2024
- How To Become A Dermatology Nurse
- How to Become a Flight Nurse
- How To Become A Hospice Nurse
- How to Become a Legal Nurse Consultant (LNC)
- How To Become A Licensed Practical Nurse?
- How To Become A Medical Assistant in 2024
- How to Become a Military Nurse
- How To Become A Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a NICU Nurse in 2024
- How To Become A Nurse Administrator
- How to Become a Nurse Anesthetist?
- How To Become A Nurse Esthetician
- How To Become A Nurse Informaticist
- How to Become a Nurse Manager
- How to Become a Nurse-Midwife
- How To Become A Phlebotomist
- How To Become A Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a Registered Nurse (RN)
- How to Become a Registered Nurse First Assistant (RNFA)
- How To Become a Surgical Nurse in 2024
- How To Become A Telemetry Nurse: Steps, Salary, Career Opportunities
- How To Become A Trauma Nurse
- How to Become A Travel Nurse in 2024
- How to Become An Acute Care Nurse Practitioner (ACNP)
- How to Become an Aesthetic/Cosmetic Nurse
- How to Become an ER Nurse in 2024
- How to Become an ICU Nurse?
- How To Become An LPN
- How To Become An Obstetrics Nurse
- How To Become An Oncology Nurse
- How To Become An Operating Room Nurse
- How To Get Your Registered Nursing License in California
- How to Go From RN to MSN?
- How To Read An Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)
- ICU Nurse Salary
- Illinois College Responses to COVID-19
- Inspiring Arizona college responses to COVID-19
- Interview with Brianna Taquinto
- Interview with Katelyn H
- Is A Surgical Nursing Career Right For You?
- Is Nursing School Really As Hard As Everyone Says?
- Labor And Delivery Nurse Salary Guide In 2024
- Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
- List of the Best Nursing Schools in Houston in 2024
- Looking for Nursing Classes Near You or Online?
- Looking for Online Nursing Programs?
- LPN Certificates vs Nursing Associate Degrees
- LPN Click
- LPN Salary in 2024
- LPN SL
- LPN To RN Program : Bridge Your Nursing Career
- LPN vs. RN Guide: Which One is Better for You?
- Massachusetts College Responses to COVID-19
- Mastering The Art Of Writing A Nursing Care Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
- Medical Assistant Salary in 2024
- Medical Assistant vs CNA
- Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Mental Health Nurse in 2024
- Missouri College Responses to COVID-19
- MSN vs. DNP Guide: Which One Is Better for You?
- Multistep
- NCLEX Lab Values Nursing Students Need To Know
- Neonatal Nurse salary in 2024
- NICU Nursing: What Every Nurse Needs to Know
- Non Clinical Nursing Jobs in 2024
- Normal Lab Values Every Nurse Should Know
- North Carolina Community College Responses to COVID-19
- Nurse Administrator Salary in 2024
- Nurse Anesthetist Salary in 2024
- Nurse Anesthetist Schooling: Your Path to Becoming a Certified CRNA
- Nurse Educator Salary in 2024
- Nurse Practitioner (NP) vs Physician Assistant (PA): Which Role is Right for You?
- Nurse Practitioner Salary in 2024
- Nurse Practitioner Salary in 2024
- Nursing Certifications in 2024
- Nursing Informatics Salary Guide
- Nursing Informatics Salary in 2024
- Nursing Requirements
- Nursing Schools in Reno NV
- Nursing Specialties in 2024
- OB-GYN Nurse Salary in 2024
- Ohio College Responses to COVID-19
- Oncology Nurse Salary in 2024
- Oregon College Responses to COVID-19
- Pediatric Nurse Salary and Career Guide: All You Need to Know
- Perioperative Nurse Salary in 2024
- Plastic Surgery Nurse Salary in 2024
- Privacy Policy
- Pros And Cons Of Being A Night Shift Nurse
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner Salary
- Psychiatric Nurse Salary
- Ranking Methodology
- Registered Nurse (RN) vs. Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
- Registered Nurse Salary in 2024
- RN Case Manager Salary in 2021
- RN Programs – Start Your Journey As A Registered Nurse
- RN to BSN Nursing Programs in PA
- RN to BSN Program Scholarship
- RN to BSN Programs in Iowa
- RN to BSN Programs in Missouri
- RN to MD: Everything You Need to Know
- Start Your Nursing Career – Free Guide
- Student Loan Forgiveness for Nurses in 2024
- Student Loan Forgiveness Programs For Nurses
- Terms of Service
- Test
- Testing123
- Thank You
- The Average Practice Nurse Salary: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Complete List of Common Nursing Certifications
- The Difference Between Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant
- The Different Nursing Levels Explained
- The Essential Skills And Qualifications To Become A Postpartum Nurse
- The Ultimate Guide to Nursing Diagnosis in 2024
- Top Paying Careers for MSN Nurses
- Trauma Nurse Salary in 2024
- Travel Nurse Salary in 2024
- Travel Nursing 101: Everything You Need To Know
- Types Of Masters Degrees In Nursing
- Types of Nursing Degrees
- Types of Nursing Specialties
- Unlocking the Potential: Advancing Your Dialysis Nurse Career
- Unraveling The Difference Between Physician Assistant And Nurse Practitioner
- Visionaries of Beauty: Discovering the Best Aesthetic Nurse Jobs
- What Are The Prerequisites For Nursing School?
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of Joining A Nurse Union?
- What Can You Do With a Nursing Degree in 2024
- What Does A CNA Do?
- What Does a Midwife Salary Look Like?
- What Does A Nurse Practitioner Do-Role And Responsibilities:
- What is a BSN Degree?
- What is a Cardiac Nurse?
- What is a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)?
- What is a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)?
- What is a Charge Nurse?
- What is a Clinical Nurse Specialist?
- What is a CNA (Certified Nursing Assistant)
- What Is A DNP Degree?
- What is a DNP in 2024
- What is a Family Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Home Health Nurse?
- What is a Hospice Nurse? | Everything You Need to Know
- What is a Labor and Delivery Nurse? | Everything You Need to Know
- What Is A Legal Nurse Consultant?
- What is a Military Nurse?
- What is a Neonatal Nurse?
- What Is A Night Shift Nurse?
- What is a Nurse Case Manager?
- What is a Nurse Practitioner in 2021
- What is a Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a PACU Nurse?
- What is a Pediatric Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Pediatric Nurse?
- What is a Physician Assistant?
- What is a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Psychiatric Nurse?
- What is a Public Health Nurse
- What is a Registered Nurse (RN)?
- What is a Registered Nurse First Assistant (RNFA)?
- What is a School Nurse? | All You Need to Know
- What is a Trauma Nurse?
- What is a Traveling Nurse?
- What is a Wound Care Nurse?
- What is an ADN? Associate Degree in Nursing Programs
- What Is an Advanced Practice Nurse
- What is an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN)?
- What Is An APRN? Understanding The Role Of An APRN
- What is an ER Nurse?
- What is an OB Nurse?
- What is an Oncology Nurse?
- What is Critical Care Nursing?
- What is Forensic Nursing?
- What Is Holistic Nursing in 2024
- What is Neonatal Nurse in 2024
- What is Nursing Informatics in 2024
- What is Nursing Informatics?
- What is Perioperative Nursing?
- What Is Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner in 2024
- What Is the difference between a CNA and an LPN?
- What is the Difference Between an LPN and RN?
- What Is the Difference Between RN and BSN Degrees?
- What is the TEAS Exam and How to Prepare For It?
- What to Expect in Nursing School Clinicals
